Surgical Stainless Steel: Properties, Applications, and Benefits
Surgical stainless steel is a specialized alloy widely used in medical, dental, and jewelry applications. Known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and strength, it plays a critical role in manufacturing surgical instruments, implants, and hypoallergenic jewelry. This article explores its composition, properties, applications, advantages, and how it compares to other stainless steel grades.
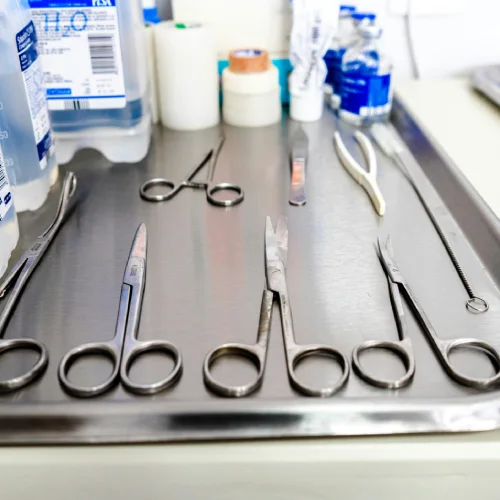
What is Surgical Stainless Steel?
Surgical stainless steel is a type of stainless steel specifically designed for medical and high-precision applications. It contains iron, chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which enhance its corrosion resistance and durability. Unlike standard stainless steel, surgical-grade alloys undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet medical industry standards.
Common surgical stainless steel grades include:
316L Stainless Steel – Preferred for implants and medical devices due to its low carbon content and superior corrosion resistance.
440 Stainless Steel – Known for its hardness, making it ideal for surgical cutting tools such as scalpels and scissors.
420 Stainless Steel – Offers good wear resistance and is often used for forceps and retractors.
Properties of Surgical Stainless Steel
1. Corrosion Resistance
One of the defining characteristics of surgical stainless steel is its high resistance to corrosion. The presence of chromium forms a passive oxide layer that protects against rust and degradation, making it suitable for prolonged exposure to body fluids, sterilization processes, and harsh chemicals.
2. Biocompatibility
Surgical stainless steel is designed to be non-reactive with human tissue, ensuring it does not cause adverse reactions when used in implants, surgical tools, or body piercings. The 316L grade, in particular, is widely used for medical implants because of its minimal nickel release, reducing the risk of allergic responses.
3. Strength and Durability
Medical instruments and implants must withstand mechanical stress and repeated sterilization. Surgical stainless steel offers excellent tensile strength and wear resistance, ensuring longevity and reliability in medical procedures.
4. Non-reactive and Hypoallergenic
For applications such as jewelry and body piercings, surgical stainless steel is valued for its hypoallergenic properties. While it contains nickel, high-quality grades release minimal amounts, making them safe for individuals with sensitive skin.
Common Applications of Surgical Stainless Steel
1. Medical Applications
Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, retractors, and scissors require high precision, hardness, and sterilization compatibility, making stainless steel an ideal choice.
Orthopedic Implants: Bone screws, plates, and joint replacements must be strong, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible to function safely within the human body.
Medical Tools & Devices: Hypodermic needles, catheters, and stents require precision manufacturing and high resistance to bodily fluids.
2. Jewelry and Body Piercings
Hypoallergenic Jewelry: Rings, earrings, and bracelets made from surgical stainless steel are popular due to their resistance to tarnishing and skin-friendly properties.
Body Piercings: High-quality 316L surgical stainless steel is widely used for piercings because it prevents infections and allergic reactions while maintaining a polished appearance.
3. Industrial and Specialized Applications
Food and Beverage Industry: Used in processing equipment and kitchen tools due to its hygienic properties.
Aerospace and Engineering: Utilized in high-precision instruments where strength and resistance to environmental factors are critical.
Surgical Stainless Steel vs. Other Stainless Steel Grades
1. 316L vs. 304 Stainless Steel
316L: Offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for implants and medical devices.
304: Common in kitchenware and general-purpose applications but lacks the same level of corrosion resistance needed for surgical use.
2. 440 vs. 420 Stainless Steel
440: Harder and more wear-resistant, suitable for cutting instruments like scalpels.
420: Less hard but provides better toughness, making it ideal for non-cutting tools like forceps.
Surgical stainless steel is an indispensable material in medical, industrial, and jewelry applications. Its superior corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and durability make it the preferred choice for surgical instruments, implants, and body piercings. Understanding its properties and proper maintenance can help ensure its effectiveness and longevity across various applications.
